Gallery details

This project builds a deep learning network to identify 102 different types of flowers. The dataset was obtained from the 102 category flowers dataset. While this specific example is used on this data, this model can be trained on any set of labeled images. Below are a few examples of the variability between classes and within the classes themselves.
CLASS VARIABILITY BETWEEN CLASSES-
The 3 images below are: (Spear Thistle) (Fire Lily) (Cantenbury Bells)

CLASS VARIABILITY WITHIN CLASSES-
Each of the 3 images below is a Toad Lily

ARCHITECTURE-
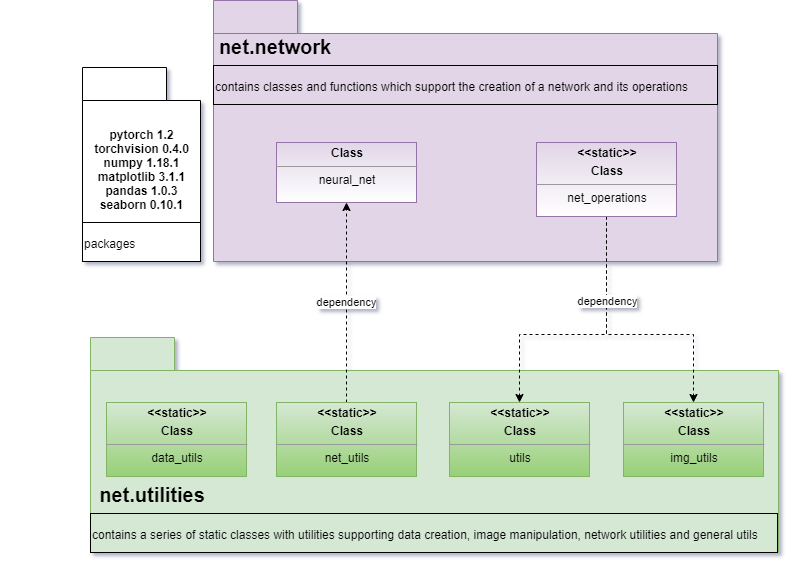
Click for Github – Project Source Code
1.DEVELOPING THE APPLICATION –
The project is broken down into multiple steps:
- Load and preprocess the image dataset
- Train the image classifier on the dataset
- Use the trained classifier to predict image content
# Imports here
import torch
import torchvision.transforms as tf
import torchvision.datasets as ds
import torchvision.models as models
from torch import nn
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
from neural_net import Neural_Network as net
# TODO: Define your transforms for the training, validation, and testing sets
# TODO: Load the datasets with ImageFolder
# TODO: Using the image datasets and the trainforms, define the dataloaders
def generate_datasets(params_dict, types_list, resize = 300, crop_size = 224):
''' Generators and data manipulation. Generates the required data transformations
for us to train properly.
Args:
params_dict (dict): The nested dictionary containing the 'dir', 'batch' and 'shuffle' data.
types_list (list of str): The list of param_dict keys, 'train', 'validate', 'test'.
resize (int): The value to resize the image to.
crop_size (int): The value we want to crop the image to
Raises:
TODO: Add exceptions
Returns:
datasets, dataloaders (tuple): The datasets and data loaders
'''
# Define the transforms
transforms = {}
for t in types_list:
transform_list = []
transform_list.append(tf.Resize(resize))
transform_list.append(tf.CenterCrop(crop_size))
transform_list.append(tf.ToTensor())
transform_list.append(tf.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]))
if t == 'train':
transform_list.pop(1)
transform_list.insert(1, tf.RandomResizedCrop(crop_size))
transform_list.insert(2, tf.RandomHorizontalFlip())
transforms[t] = tf.Compose(transform_list)
# Load the data sets, use dict comprehension to generate key vals for each type
datasets = {i: ds.ImageFolder(params_dict[i]['dir'],
transforms[i]) for i in types_list}
# Define the loaders using the datasets and the transforms
dataloaders = {i: torch.utils.data.DataLoader(datasets[i],
params_dict[i]['batch'],
params_dict[i]['shuffle'])
for i in types_list}
return datasets, dataloaders
data_dir = 'flowers'
train_dir = data_dir + '/train'
valid_dir = data_dir + '/valid'
test_dir = data_dir + '/test'
# generate datasets and loaders
params_dict = {'train': {'dir': train_dir, 'batch': 64, 'shuffle': True},
'validate':{'dir': valid_dir, 'batch': 64, 'shuffle': True},
'test':{'dir': test_dir, 'batch': 64, 'shuffle': False}}
datasets, dataloaders = generate_datasets(params_dict, list(params_dict.keys()))
# build network
class Neural_Network(nn.Module):
'''
The neural network object sits a level above the classifier to
store relevant properties and values. The classifier uses nn.LogSoftmax so use the
negative log likelihood loss criterion nn.NLLLoss
Args:
inputs (int): The number of inputs.
hidden_sizes (list of ints): The hidden layer sizes.
outputs (int): The number of outputs.
hidden_activation (str): The hidden layer activation functions (ex. relu, sigmoid, tahn).
device (str): The gpu or the cpu.
optimizer_name (str): The optimizer name ('sgd' or 'adam') to update the weights and gradients
dropout (float): The dropout rate, value to randomly drop input units through training.
learn_rate (float): The learning rate value, used along with the gradient to update the weights,
small values ensure that the weight update steps are small enough.
Attributes:
inputs (int): This is where we store the input count,
hidden_sizes (list of int): This is where we store the hidden layer sizes,
outputs (int): This is where we store the output size,
hidden_activation (str): This is where we store the hidden activation type,
dropout (float): This is where we store the random input unit dropout rate,
learn_rate (float): This is where we store the learn rate value,
processing_device (str): This is where we store the device to calculate the results,
linear_layers (list): This is where we store the values to sequentially build the classifier,
model (torch.nn.module or torchvision model): Where either the generated classifier or the loaded model is stored,
optimizer (torch.optim): This is where we store the optimizer used,
criterior (torch.nn.module.loss): This is where we store the loss function type,
device (str): This is where we store the device,
epochs_completed (int): This is where we store how many total epochs of training this model has.
'''
def __init__(self, inputs, hidden_sizes,
outputs, hidden_activation, device,
dropout = 0.3, learn_rate = 0.002):
super().__init__()
# Props
self.inputs = inputs
self.hidden_sizes = hidden_sizes
self.outputs = outputs
self.hidden_activation = hidden_activation
self.dropout = dropout
self.learn_rate = learn_rate
self.processing_device = device
# Layers
self.linear_layers = []
self.data = hidden_sizes
self.data.insert(0,inputs)
self.data.append(outputs)
# Model Stuff
self.model, self.optimizer = None, None
self.criterion = nn.NLLLoss()
self.device = device
self.epochs_completed = 0
self.generate_classifier()
def generate_classifier(self):
'''Generates the nn.module container Sequential classfier as the default for this class.
Args:
None.
Raises:
TODO: Update exceptions with error_handling class.
Returns:
None.
'''
self.linear_layers = []
n = len(self.data)
for i in range(n-1):
self.linear_layers.append(nn.Linear(self.data[i],self.data[(i + 1) % n]))
if i != n-2:
if self.hidden_activation == 'relu':
self.linear_layers.append(nn.ReLU())
elif self.hidden_activation == 'sigmoid':
self.linear_layers.append(nn.Sigmoid())
elif self.hidden_activation == 'tanh':
self.linear_layers.append(nn.Tanh())
self.linear_layers.append(nn.Dropout(self.dropout))
self.linear_layers.append(nn.LogSoftmax(dim = 1))
# expand the list into sequential args
self.model = nn.Sequential(*self.linear_layers)
def train_network(self, train_data, validation_data, epochs = 1, load_best_params = False, plot = False):
'''Trains the model, requires the criterion and optimizer to be passed into the class args before hand.
TODO: add exception handling for optimizer and criterion as None values.
Args:
train_data (torch.utils.data.dataloader.DataLoader): The training torch data loader.
validation_data (torch.utils.data.dataloader.DataLoader): The validation torch data loader.
epochs (int): The number of epochs for training.
load_best_params (bool): If true then we will load the model_state_dict from the highest accuracy iteration
plot (bool): If true we plot both losses.
Raises:
TODO: Add exceptions.
Returns:
None.
'''
# move the model to whatever device we have
self.model.to(self.device)
# if we loaded the model in eval mode and want to train switch it
if not self.model.training:
self.model.train()
iteration, running_loss = 0, 0
highest_accuracy, high_acc_iter, high_acc_epoch = 0, 0, 0
training_loss_set, validation_loss_set = [], []
best_params = None
for epoch in range(epochs):
batch_iteration = 0
for x, y_labels in train_data:
# move to whatever device we have
x, y_labels = x.to(self.device), y_labels.to(self.device)
# zero out the gradients
self.optimizer.zero_grad()
# forward pass - get the log probabilities (logits / scores)
output = self.model(x)
# calculate the loss
loss = self.criterion(output, y_labels)
# backprop - calculate the gradients for the parameters
loss.backward()
# parameter update based on gradient
self.optimizer.step()
# update stats
running_loss += loss.item()
iteration += 1
batch_iteration += 1
else:
# Validation Process
validation_loss, accuracy = self.validate_network(validation_data)
training_loss = running_loss/len(train_data)
print('Model has a total of {} training epochs completed.'.format(self.epochs_completed))
print('Active session Epoch {} out of {}'.format(epoch + 1, epochs))
print('Currently model has Accuracy of {}% \nCurrent training loss is {} \
\nCurrent validation loss is {}'.format(accuracy,
training_loss, validation_loss))
training_loss_set.append(training_loss)
validation_loss_set.append(validation_loss)
print('-------------')
running_loss = 0
# Track best run
if accuracy > highest_accuracy:
highest_accuracy = accuracy
high_acc_iter = batch_iteration
high_acc_epoch = epoch + 1
if load_best_params:
best_params = copy.deepcopy(self.model.state_dict())
# Set the model back to train mode, enable dropout again
self.model.train()
self.epochs_completed += 1
t_slope, v_slope = self.check_overfitting(training_loss_set, validation_loss_set, plot)
print('Slope of linear reg training curve fit is {} \nSlope of linear reg Validation curve fit is {}'.format(t_slope,
v_slope))
print('Training session highest accuracy was {} on epoch {} batch iteration {}'.format(highest_accuracy,
high_acc_epoch,
high_acc_iter))
if load_best_params:
self.model.load_state_dict(best_params)
print('Params from {} epoch, {} batch iteration were loaded'.format(high_acc_epoch, high_acc_iter))
def validate_network(self, data):
'''Validate our model to check the loss and accuracy.
Args:
data (torch.utils.data.dataloader.DataLoader): The data we want to validate as torch data loader.
Raises:
TODO: Add exceptions.
Returns:
loss,accuracy (tuple): The loss and accuracy of the validation.
'''
# enable eval mode, turn off dropout
self.model.eval()
# turn off the gradients since we are not updating params
with torch.no_grad():
batch_loss = 0
batch_accuracy = 0
# validation pass
for x, y_labels in data:
# move to device
x, y_labels = x.to(self.device), y_labels.to(self.device)
output = self.model(x)
# update loss and extract tensor as python float
batch_loss += self.criterion(output, y_labels).item()
# calculate the probability
probability = torch.exp(output)
# get the top n indexes and values
_, top_class = probability.topk(1, dim=1)
# reshape top class to match label and get binary value from equals,
# check if the prediction matches label
equals = top_class == y_labels.view(*top_class.shape)
# have to convert byte tensor to float tensor and get accuracy
batch_accuracy += torch.mean(equals.type(torch.FloatTensor)).item()
test_accuracy = (batch_accuracy / len(data))*100
test_loss = batch_loss / len(data)
return test_loss, test_accuracy
def check_overfitting(self, train_losses, validation_losses, plot = False):
'''Validate our model to check the loss and accuracy
Args:
train_losses (list of floats): The list of training losses per epoch.
validation_losses (list of floats): The list of validation losses per epoch.
plot (bool): If true we plot both losses.
Raises:
TODO: Add exceptions.
Returns:
slopes (tuple): The slopes of the linear reg curve fits for both validation/training.
'''
# Data
tl_x_val = np.arange(0, len(train_losses))
vl_x_val = np.arange(0, len(validation_losses))
# To numpy
train_data = np.array([tl_x_val, train_losses])
validate_data = np.array([vl_x_val, validation_losses])
# Least squares polynomial fit.
train_slope, train_intercept = np.polyfit(train_data[0], train_data[1], 1)
validation_slope, validation_intercept = np.polyfit(validate_data[0], validate_data[1], 1)
if plot:
plt.plot(train_data[0], train_data[1], 'o', label='training loss')
plt.plot(validate_data[0], validate_data[1], 'o', label='validation loss')
plt.plot(train_data[0], train_intercept + train_slope*train_data[0], 'r', label='train_regg')
plt.plot(validate_data[0], validation_intercept + validation_slope*validate_data[0], 'r', label='val_regg')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
return train_slope, validation_slope
def save_model_checkpoint(self, full_path, training_class_to_idx):
'''Save the model checkpoint.
Args:
full_path (str): The full path to save the checkpoint to
training_class_to_idx (dic of ints): This is where we store the dictionary mapping the name of the class to the index (label)
Raises:
TODO: Add exceptions
Returns:
None
'''
net_data_dic = {'input_count': self.inputs,
'hidden_sizes': self.hidden_sizes,
'outputs': self.outputs,
'h_activation': self.hidden_activation,
'dropout': self.dropout,
'learn_rate': self.learn_rate,
'epochs_completed' : self.epochs_completed}
checkpoint = {'data' : net_data_dic,
'model' : self.model,
'classifier' : self.model.classifier,
'optimizer.state_dict' : self.optimizer.state_dict(),
'state_dict' : self.model.state_dict(),
'device' : self.device,
'class_to_idx': training_class_to_idx}
torch.save (checkpoint, full_path)
# Net Utilities to build from tv
def net_from_torchvision(hidden_sizes, outputs, hidden_activation, device,
optimizer_name = 'adam', dropout = 0.3, learn_rate = 0.002,
name = 'vgg16', trained = True):
'''
Generates a model from torchvision, and instatiates a new Neural_Network instance which sets new model
as the active model. A new optimizer and criterion are also generated and assigned to the class properties.
Args:
hidden_sizes (list of ints): The hidden layer sizes.
outputs (int): The number of outputs.
hidden_activation (str): The hidden layer activation functions (ex. relu, sigmoid, tahn).
device (str): The gpu or the cpu.
optimizer_name (str): The optimizer name ('sgd' or 'adam') to update the weights and gradients
dropout (float): The dropout rate, value to randomly drop input units through training.
learn_rate (float): The learning rate value, used along with the gradient to update the weights,
small values ensure that the weight update steps are small enough.
name (str): The pretrained model name ('vgg16', 'resnet50', 'densenet121').
trained (bool): If the model has been trained.
Raises:
TODO: Update exceptions with error_handling class.
Returns:
net (nn_model.Neural_Network): An instance of the Neural_Network class with the trained model
as its model and parameters.
'''
model = get_pretrained_model(name, trained)
feature_count = model.classifier[0].in_features
net = Neural_Network(feature_count, hidden_sizes, outputs,
hidden_activation, device, dropout, learn_rate)
model.classifier = net.model
net.model = model
if optimizer_name != 'adam' and optimizer_name != 'sgd':
raise ValueError('Please use either SDG or Adam as optimizers')
elif optimizer_name == 'adam':
net.optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(net.model.classifier.parameters(), learn_rate)
else:
net.optimizer = torch.optim.SDG(net.model.classifier.parameters(), learn_rate)
net.criterion = nn.NLLLoss()
return net
def get_pretrained_model(name = 'vgg16', trained = True):
'''Generates the nn.module container Sequential classfier as the default for this class.
Args:
name (str): The pretrained model name ('vgg16', 'resnet50', 'densenet121').
trained (bool): If the model has been trained.
Raises:
TODO: Update exceptions with error_handling class.
Returns:
model (torchvision.models.vgg.VGG): The torch vision model specified
'''
# get model from torchvision
if name == 'vgg16':
model = models.vgg16(pretrained = trained)
elif name == 'resnet50':
model = models.resnet50(pretrained = trained)
elif name == 'densenet121':
model = models.densenet121(pretrained = trained)
else:
raise ValueError('Please select from either vgg16, resnet50 or \
densenet121 pre-trained models')
# freeze parameters
for parameter in model.parameters():
parameter.requires_grad = False
return model
# TODO: Write a function that loads a checkpoint and rebuilds the model
def load_neural_net(filepath, mode = 'train'):
'''
Generates a model from torchvision, and instatiates a new Neural_Network instance which sets new model
as the active model. A new optimizer and criterion are also generated and assigned to the class properties.
Args:
file_path (str): The full path to the checkpoint
mode (str): Mode to set the model to ('train', 'eval')
Raises:
TODO: Update exceptions with error_handling class.
Returns:
net (nn_model.Neural_Network): An instance of the Neural_Network class with the loeaded model
as its model, parameters, criterion and optimizer.
'''
print('loading_net')
#TODO: Path validation
checkpoint = torch.load(filepath)
# Set Params
inputs = checkpoint['data']['input_count']
hidden_layers = checkpoint['data']['hidden_sizes']
outputs = checkpoint['data']['outputs']
activation = checkpoint['data']['h_activation']
dropout = checkpoint['data']['dropout']
learn_rate = checkpoint['data']['learn_rate']
device = checkpoint['device']
model = checkpoint['model']
model.load_state_dict(checkpoint['state_dict'])
# Make Network
net = Neural_Network(inputs, hidden_layers, outputs, activation, device, dropout, learn_rate)
net.model = model
net.epochs_completed = checkpoint['data']['epochs_completed']
if mode == 'train':
net.model.train()
elif mode == 'eval':
net.model.eval()
else:
raise ValueError('Error mode needs to be either train or eval')
net.model.classifier.class_to_idx = checkpoint['class_to_idx']
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(net.model.classifier.parameters(), learn_rate)
optimizer.load_state_dict(checkpoint['optimizer.state_dict'])
criterion = nn.NLLLoss()
net.optimizer = optimizer
net.criterion = criterion
# Move to processing device
net.model.to(device)
return net
# load the model
loaded_net = load_neural_net('checkpoint_1.pth', 'eval')
# process image
def process_image(image, width, height):
''' Scales, crops, and normalizes a PIL image for a PyTorch model,
returns an torchNumpy array
Args:
image (nn_model.Neural_Network): The Neural_Network instance to use for the prediction.
width (int): The path to the image we want to test
height (int): The label map with the class names
Raises:
TODO: Add exceptions
Returns:
t_image (torch.Tensor):
'''
# open and resize
img = Image.open(image)
img = img.resize((width,height))
# crop
current_width, current_height = img.size
left = (current_width - width)/2
top = (current_height - height)/2
right = left + width
bottom = top + height
img = img.crop((left, top, right, bottom))
# normalize the values
mean = np.array([0.485, 0.456, 0.406])
std = np.array([0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
np_img = np.array(img) / 255
np_img = (np_img - mean) / std
# swap color channel position
np_img = np.transpose(np_img, (2,0,1))
# conver to tensor from numpy ndarray
t_image = torch.from_numpy(np_img)
return t_image
def map_idx_to_classes(class_to_idx, classes, predicted_idx, predicted_prob):
'''
Maps the predicted indexes to the keys which we need to retrieve the class names. Since our model gives us the 'value',
we need to find the key for our class_to_idx dict, once we have the key we can use it to find the class mapping
(flower name in this case).
Args:
class_to_idx (dic of ints): This is where we store the dictionary mapping the name of the class to the index (label).
classes (dict of strs): Dict containing the mapping of the class idx to the name.
predicted_idx (list of ints): The topk list of predicted indexes.
predicted_prob (list of floats): The probability list from topk.
Raises:
TODO: Update exceptions with error_handling class.
Returns:
idx_classes_dict (dict): Dictionary containing 'predicted_indexes': indexes predicted by network,
'idx_to_class': mapped idx_to_class,
'classes': class names,
'probabilites': the probabilities for classes.
'''
idx_classes_dict = {}
predicted_class_names = []
predicted_idx_to_class = []
for x in predicted_idx:
for k,v in class_to_idx.items():
if x == v:
predicted_class_names.append(classes[k])
predicted_idx_to_class.append(k)
idx_classes_dict['predicted_idx'] = predicted_idx
idx_classes_dict['classes'] = predicted_class_names
idx_classes_dict['idx_to_class'] = predicted_idx_to_class
idx_classes_dict['probabilities'] = predicted_prob
return idx_classes_dict
# helper methods
def predict(network, image_path, class_names, topk=5):
''' Predict the class (or classes) of an image using a trained deep learning model.
Args:
network (nn_model.Neural_Network): The Neural_Network instance to use for the prediction.
image_path (str): The path to the image we want to test
class_names (dict of ints): The label map with the class names
topk (int): The number of top probabilities and classes we want.
Raises:
TODO: Add exceptions
Returns:
data_dict (dict): Dictionary containing 'predicted_indexes': indexes predicted by network,
'idx_to_class': mapped idx_to_class,
'classes': class names,
'probabilites': the probabilities for classes.
'''
# convert image
img = process_image(image_path, 224, 224)
# need to pass the image tensor with first argument of n where n represents our batch size
img.unsqueeze_(0)
# move to device
img.to(network.device)
# generate the prediction
network.model.to(network.device)
# enable eval mode, turn off dropout
network.model.eval()
# turn off the gradients since we are not updating params
with torch.no_grad():
img = img.to(network.device, dtype=torch.float)
# get the log softmax
output = network.model(img)
# get the prob
probabilities = torch.exp(output)
# get the top k values
top_probabilities, top_classes = probabilities.topk(topk, dim=1)
# remove the tensor cuda by moving to cpu, squeeze to remove dimensions and send to list to index
top_probabilities = top_probabilities.cpu().squeeze().tolist()
top_classes = top_classes.cpu().squeeze().tolist()
# generate the idx_to_class mapping dict
data_dict = map_idx_to_classes(network.model.classifier.class_to_idx, class_names, top_classes, top_probabilities)
return data_dict
# TODO: Display an image along with the top 5 classes
# To visualize more than 1 result at a time I added this function, displays a grid of n results with image and prediction
import numpy as np
import seaborn as sb
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
def plot_image_results(datasets, filter, count):
# generate random n indexes to choose random testing images from dataset
idx = np.random.randint(0,len(datasets[filter].imgs),size=(count,))
print(idx)
# get the image folder number idx from the randomly selected dataset image
batch_idx = [datasets[filter].imgs[x][0].split('\\')[-2] for x in idx]
print(batch_idx)
# fix the full path for the batch idx's
batch_paths = [datasets[filter].imgs[x][0].replace('\\','/') for x in idx]
print(batch_paths)
# get actual flower name from the mapping back to the label
labeled_names = [flowers_to_name[x] for x in batch_idx]
print(labeled_names)
# zip the data
data = dict(zip(labeled_names, batch_paths))
# set the subplots
rows = (len(data.items()))
cols = 2
fig, axs = plt.subplots(nrows = rows, ncols= cols, figsize=(cols*4,rows*3), squeeze = False)
axs = axs.flatten()
plt.tight_layout()
# iterate through the dict, plot the graphs on the even grid cell
# plot matching imgs on the odd grid cells
count, img_counter = 0, 1
for name, path in data.items():
# get the predictions
results_dict = predict(loaded_net, path, flowers_to_name)
for k,v in results_dict.items():
print('{}:{}'.format(k, v))
print('flower is {}\n'.format(name))
# barplots for the results
bp = sb.barplot(x=results_dict['probabilities'], y=results_dict['classes'], ax=axs[count])
bp.set_title(name)
# plot the images
img = process_image(path, 224, 224)
imshow(img, axs[img_counter])
# increment the counters
count += 2
img_counter += 2
plt.show()
plot_image_results(datasets, 'test', 5)
.Build and train network –
Building and training the classifier:
- Load a pre-trained network
- Define a new, untrained feed-forward network as a classifier, choose activation functions and dropouts
- Train the classifier layer using backpropagation using the pre-trained network to get the features
- Track the loss and accuracy on the validation set to determine the best hyperparameters
# TODO: Build and train your network
# check for gpu
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
# network instance
neural_net = net_from_torchvision([1024,512], 102, 'relu', device, learn_rate = 0.001)
# train for 25 epochs
neural_net.train_network(dataloaders['train'], dataloaders['validate'], 5, plot = True)
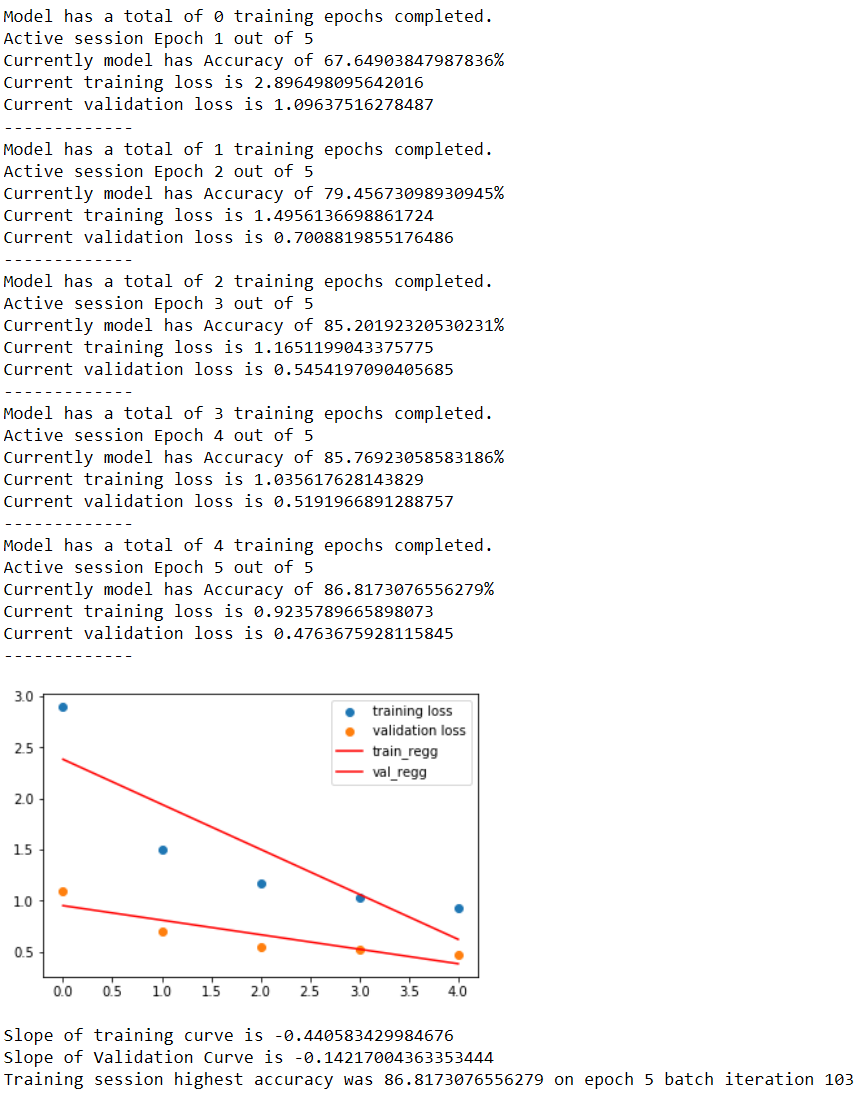
.Test the network-
# TODO: Do validation on the test set
loss, acc = neural_net.validate_network(dataloaders['test'])
print('acc on test is {} % \nloss is {}'.format(acc, loss))
img_path = 'flowers/test/15/image_06360.jpg'
# get the predictions
results_dict = predict(loaded_net, img_path, flowers_to_name)
for k,v in results_dict.items():
print('{}:{}'.format(k, v))
""" OUTPUT
predicted_idx:[9, 62, 45, 39, 48]
classes:['yellow iris', 'black-eyed susan', 'buttercup', 'daffodil', 'common dandelion']
idx_to_class:['15', '63', '48', '42', '50']
probabilities:[0.9235654473304749, 0.04405064508318901, 0.015102370642125607, 0.010496463626623154, 0.001698569511063397]
"""
# get flower names fromr results dict
print(results_dict['idx_to_class'])
names = [flowers_to_name[x] for x in results_dict['idx_to_class']]
print(names)
""" OUTPUT
['15', '63', '48', '42', '50']
['yellow iris', 'black-eyed susan', 'buttercup', 'daffodil', 'common dandelion']
"""
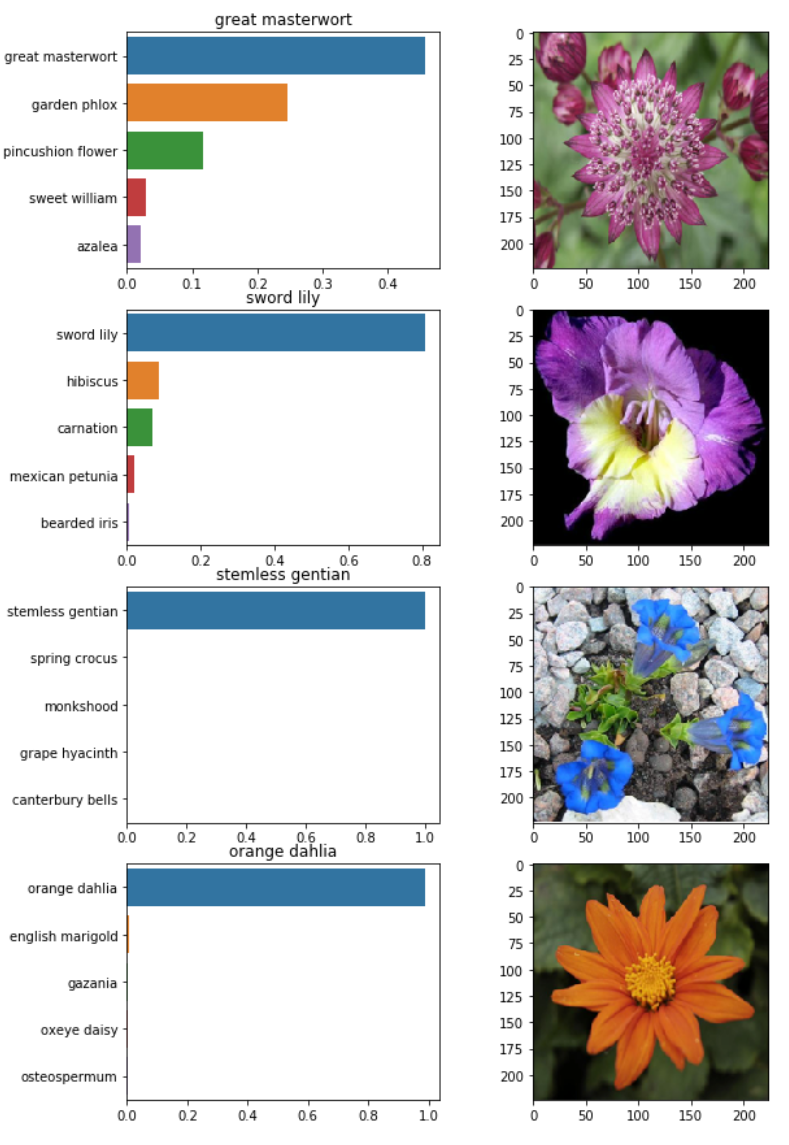
plot_image_results(datasets, 'test', 5)
.Plot Results-
To visualize more than 1 result at a time I added this function, displays a grid of n results with image and prediction
2.COMMAND LINE APPLICATION SPECIFICATIONS –
The project submission must include at least two files train.py and predict.py. The first file, train.py, will train a new network on a dataset and save the model as a checkpoint. The second file, predict.py, uses a trained network to predict the class for an input image.
-
- Train a new network on a data set with train.py :
- Basic usage:
python train.py data_directory - Prints out training loss, validation loss, and validation accuracy as the network trains
- Options:
- Set directory to save checkpoints:
- python train.py data_dir –save_dir save_directory
- Choose architecture:
python train.py data_dir --arch "vgg13" - Set hyperparameters:
- python train.py data_dir –learning_rate 0.01 –hidden_units 512 –epochs 20
- Use GPU for training:
python train.py data_dir --gpu
- Set directory to save checkpoints:
- Basic usage:
- Predict flower name from an image with
predict.pyalong with the probability of that name. That is, you’ll pass in a single image/path/to/imageand return the flower name and class probability.- Basic usage:
python predict.py /path/to/image checkpoint - Options:
- Return top K most likely classes:
- python predict.py input checkpoint –top_k 3
- Use a mapping of categories to real names:
- python predict.py input checkpoint –category_names cat_to_name.json
- Use GPU for inference:
python predict.py input checkpoint --gpu
- Return top K most likely classes:
- Basic usage:
- Train a new network on a data set with train.py :
import argparse
import json
import torch as t
import os
import sys
from network.net_operations import Net_Operations as net_ops
from utilities.net_utils import Net_Utilities as net_utils
from utilities.utils import Utilities as utils
'''predict.py: Predict a flower name from an image along with the probability of that name '''
__author__ = "Luis Quinones"
__email__ = "luis@complicitmatter.com"
__status__ = "Prototype"
def main():
try:
args_dict = {}
names = ['image_path', 'model_checkpoint_path', '--top_k', '--category_names', '--gpu']
defaults = [None, None, 3, 'flower_to_name.json', False]
types = [str, str, int, str, bool]
helpers = ['the path to the image we want to predict',
'the path to the model checkpoint to load',
'return the top k most likely cases',
'Json file with the mapping of categories to real names',
'Use the gpu for computing, if no use cpu']
for i in range(len(names)):
data = {}
data['name'] = names[i]
data['default'] = defaults[i]
data['type'] = types[i]
data['help'] = helpers[i]
args_dict[i] = data
# get the args
args = utils.get_input_args(args_dict)
# variables
img_path = args.image_path
model_checkpoint = args.model_checkpoint_path
top_k = args.top_k
categories = args.category_names
enable_gpu = args.gpu
# check if the img path exist
while not os.path.isfile(img_path):
img_path = input('Image file does not exist, please input a correct path \n')
if img_path == 'quit':
exit()
# check if the checkpoint file exist
while not os.path.isfile(model_checkpoint):
model_checkpoint = input('Model checkpoint does not exist, please input a correct path \n')
if model_checkpoint == 'quit':
exit()
while top_k < 1:
val = input('Top_k value must be greater than 0, please enter a new value \n')
top_k = int(val)
# check for gpu
if not t.cuda.is_available() and enable_gpu:
print('Your device does not have a CUDA capable device, we will use the CPU instead')
response = input('Your device does not have a CUDA capable device, would you like to run it on the CPU instead? Enter Yes or No -> ')
while response not in ('yes', 'no'):
if response.lower() == 'yes':
break
elif response.lower() == "no":
print('exiting the program')
exit()
else:
print('Please respond yes or no ')
enable_gpu = False
# load from checkpoint and set device
mfcp = net_utils.load_neural_net(model_checkpoint, 'eval')
mfcp.device = 'cuda' if enable_gpu else 'cpu'
# load json data
with open(categories, 'r') as f:
categories_to_name = json.load(f)
# make the predictions
results_dict = net_ops.predict(mfcp, img_path, categories_to_name, topk = top_k)
names = [categories_to_name[x] for x in results_dict['idx_to_class']]
# get flower name from path
flower_name = categories_to_name[img_path.split('/')[-2]]
# print the top n results
print('FLOWER NAME IS {} \n'.format(flower_name.upper()))
print('THE TOP {} RESULTS ARE:'.format(top_k))
for i, name in enumerate(names):
print('Name = {} \nProbability = {} \n'.format(name, results_dict['probabilities'][i]))
except Exception as ex:
raise ex
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
import argparse
import sys
from collections import defaultdict
import os
import datetime
import torch as t
from utilities.utils import Utilities as utils
from utilities.net_utils import Net_Utilities as net_utils
from utilities.data_utils import Data_Utilities as data_util
'''train.py: Train a new network on a dataset of images '''
__author__ = "Luis Quinones"
__email__ = "luis@complicitmatter.com"
__status__ = "Prototype"
def main():
try:
args_dict = {}
names = ['data_dir', '--save_dir', '--arch', '--learning_rate', '--hidden_units', '--epochs', '--gpu']
def_save_path = os.getcwd() + '/checkpoint_nn_train.pth'
def_save_path = def_save_path.replace('\\','/')
defaults = [None, def_save_path, 'vgg16', 0.001, '1024, 512', 2, False]
types = [str, str, str, float, str, int, bool]
helpers = ['the directory of the data, ex. flowers/',
'the fullpath with name where we want to save our checkpoints, ex. saved/checkpoint_xx.pth',
'the architecture to transfer learning, vgg16, resnet50, densenet121',
'the learning rate value',
'the values for the hidden layer sizes form ex. 1024,512',
'the number of epochs to train',
'Use the gpu for computing, if no use cpu']
for i in range(len(names)):
data = {}
data['name'] = names[i]
data['default'] = defaults[i]
data['type'] = types[i]
data['help'] = helpers[i]
args_dict[i] = data
# get the args
args = utils.get_input_args(args_dict)
# variables
directory = args.data_dir
if not os.path.exists(directory):
raise OSError('Directory does not exist, please specify a new one')
checkpt_dir = args.save_dir
arch = args.arch
learn_rate = args.learning_rate
hidden_layers = args.hidden_units
epochs = args.epochs
enable_gpu = args.gpu
trim = hidden_layers.strip('[]').split(',')
hidden_layers = [int(i) for i in trim]
# check for gpu
if not t.cuda.is_available() and enable_gpu:
print('Your device does not have a CUDA capable device, we will use the CPU instead')
response = input('Your device does not have a CUDA capable device, would you like to run it on the CPU instead? Enter Yes or No -> ')
while response not in ('yes', 'no'):
if response.lower() == 'yes':
break
elif response.lower() == "no":
print('exiting the program')
exit()
else:
print('Please respond yes or no ')
enable_gpu = False
# generate datasets
params_dict = {'train': {'dir': directory + 'train', 'batch': 64, 'shuffle': True},
'validate':{'dir': directory + 'valid', 'batch': 64, 'shuffle': True}}
datasets, dataloaders = data_util.generate_datasets(params_dict, list(params_dict.keys()))
# network instance
processor = 'cuda' if enable_gpu else 'cpu'
neural_net = net_utils.net_from_torchvision(hidden_layers, 102, 'relu', processor, learn_rate = learn_rate, name = arch)
# train for n epochs
neural_net.train_network(dataloaders['train'], dataloaders['validate'], epochs, plot = True)
# save model
neural_net.save_model_checkpoint(checkpt_dir, datasets['train'].class_to_idx)
except Exception as ex:
raise ex
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
.Test command line application-
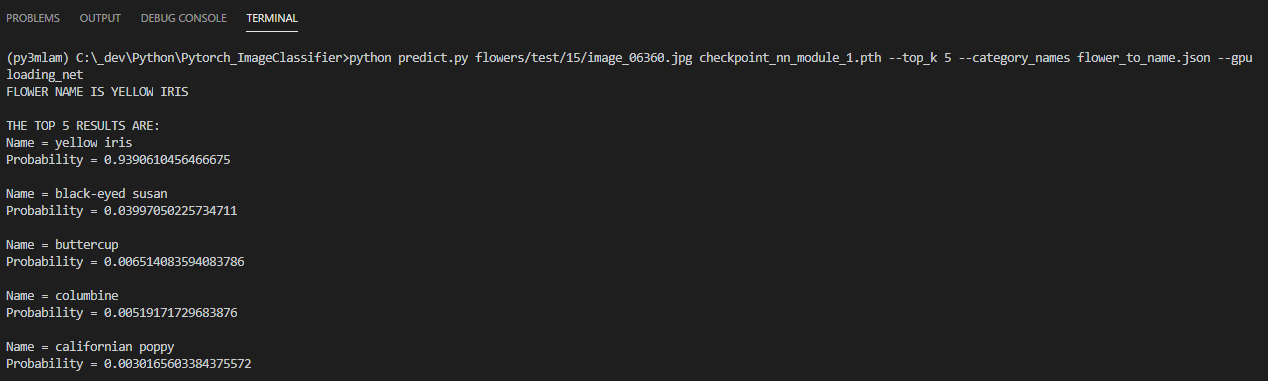
Recently in Portfolio
- [K]ernels

- Nike A.I.R Prototypes

- [A]nisochromatic Meshing

- Nike After Dark Tour

- PARAPRAXIS
- [001.HRR] CONCEPT BIKE

- 2040:LUNAR.OUTPOST[a]
- HE.6 2020 Prototype

- CULEBRA.NET

- PYTORCH-CLASSIFIER
- Nike Zoom Superfly Elite

- BENGBU CITY OPERA

- Nike Footscape Flyknit DM

- Jordan Hyperdunk React

- KA-HELMET

- [C]ucarachas

- [S]eeker
- [O]h Baby
- [E]l Papa

- [S]hatter.Brain

- [S]tigmergy
- [F]orces
- CULEBRA.JAVA

- [C]ulebra.MultiBehaviors

- [S]ticky Stuff
- [S]entinels
- [G]allopingTopiary
- RELUXOED

- [SRC] . Semi Rigid Car

- [P]erlin

- [E]ternal Wanderers
- [W]heelie

- [S]labacube

- [M]esh Crawlers

- [L]a Silla
- [3]D BabyMaking Trackstars
- [3]D Trackers
- [2]D BabyMaking Trackers
- [T]rackers
- CULEBRA GRASSHOPPER

- culebra.[M]eshCrawlers.3D

- culebra.[H]ybrid.3D

- culebra.[F]lorgy

- culebra.[F]ockers.3D
- culebra.[F]ockers.2D

- culebra.[N]oisey.3D

- [E]l Nino

- culebra.[S]elfOrg

- [D]rippin

- culebra.[N]oisey.2D

- [C]reepyCrawlers

- [J]eepresesCreepers

- [T]2000

- PUFFER PLEATNESS

- EMERGEN[CY]

- [L]iquified

- [S]uckedComp

- [X]plosion
- MR. EW

- [H]airGoo
- [B]alled
- [n]injaStars

- [b]loomer

- [t]rip city

- TAPE GUNNED
- [B]oom

- [M]iller Time
- [D]elamjam

- [B]rain Zapper
- [B]ig Bird
- [E]gg Tube Pavillion
- [A]llice’s Easter Tree
- [S]weet Honey
- [U]M.Urgent

- [t]oo.urgent

- [B]onnie..+..Clyde
- [B]io Mess
- [EL]Mojado.Virus
- [W]HAT the …!
- [H]ot Lava
- [P]leat Diddy
- [t]erminator easter egg
- Mr. BB
- [B]less You

- [F]antastic + Interactive
- [S]oo_Minimally_Pathed
- [P]uffer Fish.Fab
- [M]an Eater

- [AHH] Alien House Hunters

- [W]eave Machine
- Sportbike Racing

- Grappling

- Kart Racing


Leave a reply