Gallery details
created at Mode Lab Experiments
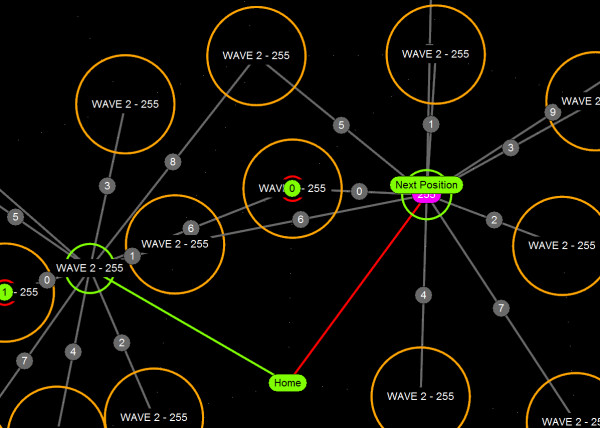
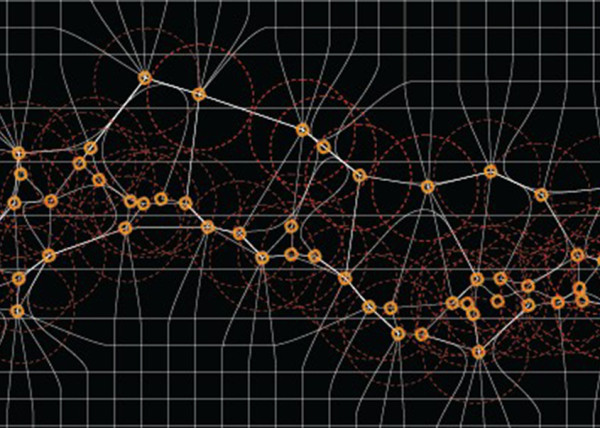
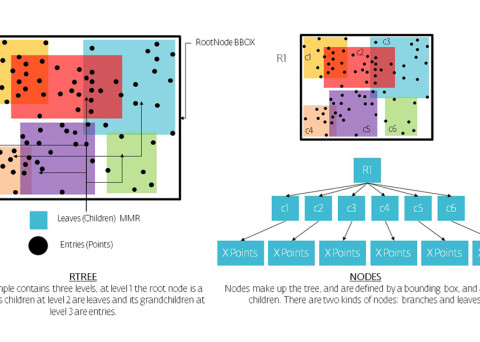
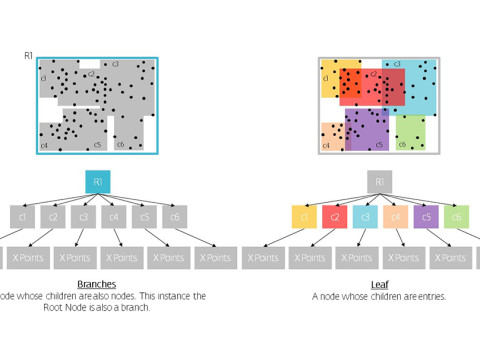
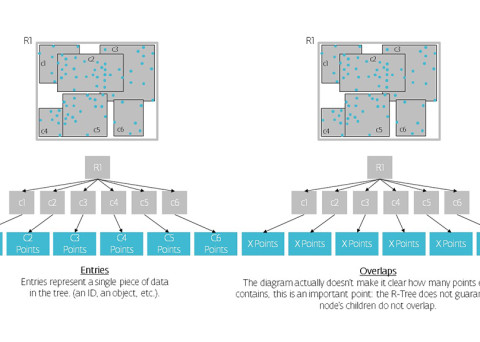
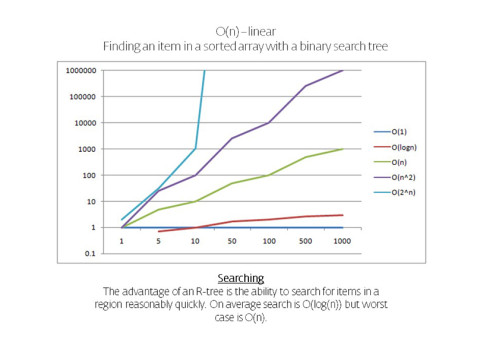
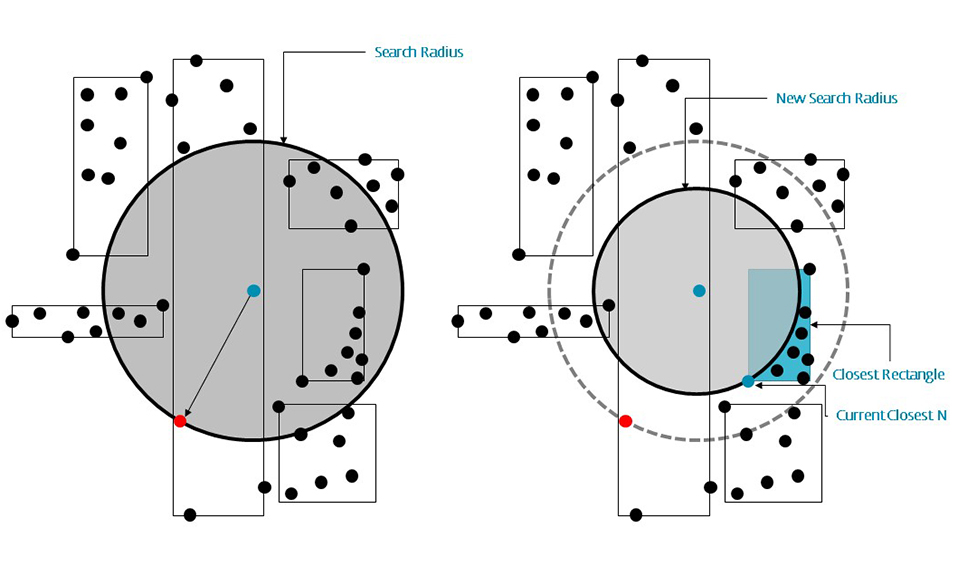
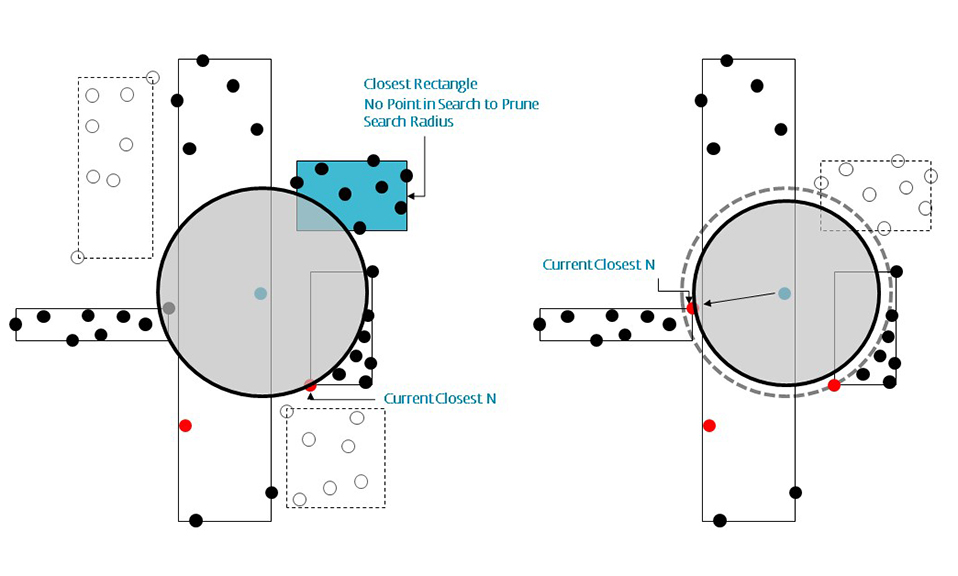
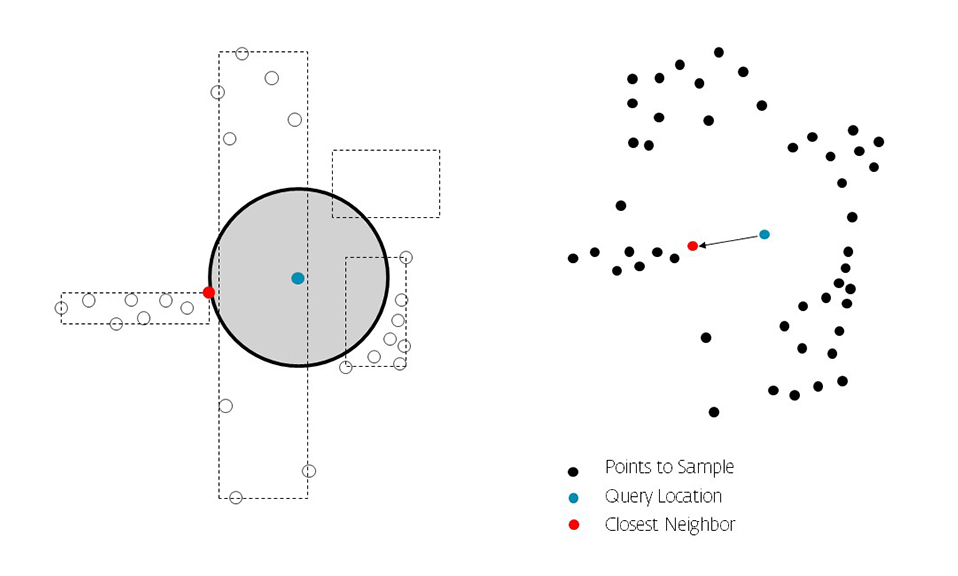
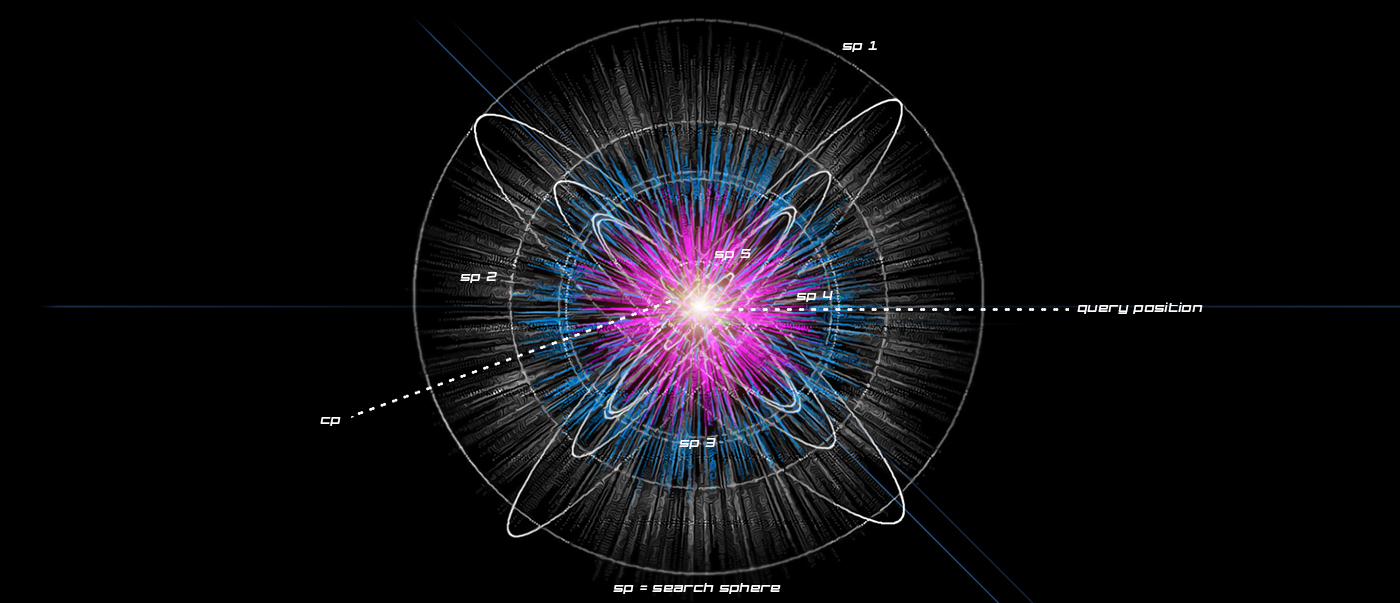
R-trees are balanced tree data structures used for spatial access methods in N-dimensional space. Implementing the RTree Class will allows us to reduce the search space by incorporating a searching sphere or bbox . R-tree is also a balanced search tree (so all leaf nodes are at the same height), organizes the data in pages, and is designed for storage on disk.
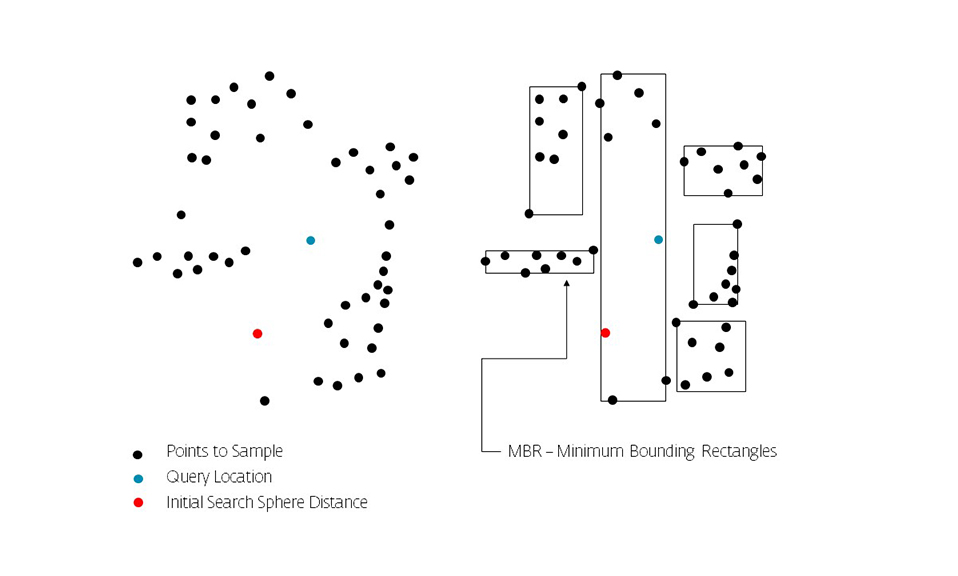
The key idea of the data structure is to group nearby objects and represent them with their minimum bounding rectangle (MBR) in the next higher level of the tree. Since all objects lie within this bounding rectangle, a query that does not intersect the bounding rectangle also cannot intersect any of the contained objects. At the leaf level, each rectangle describes a single object; at higher levels the aggregation of an increasing number of objects. This can also be seen as an increasingly coarse approximation of the data set. – Wikipedia
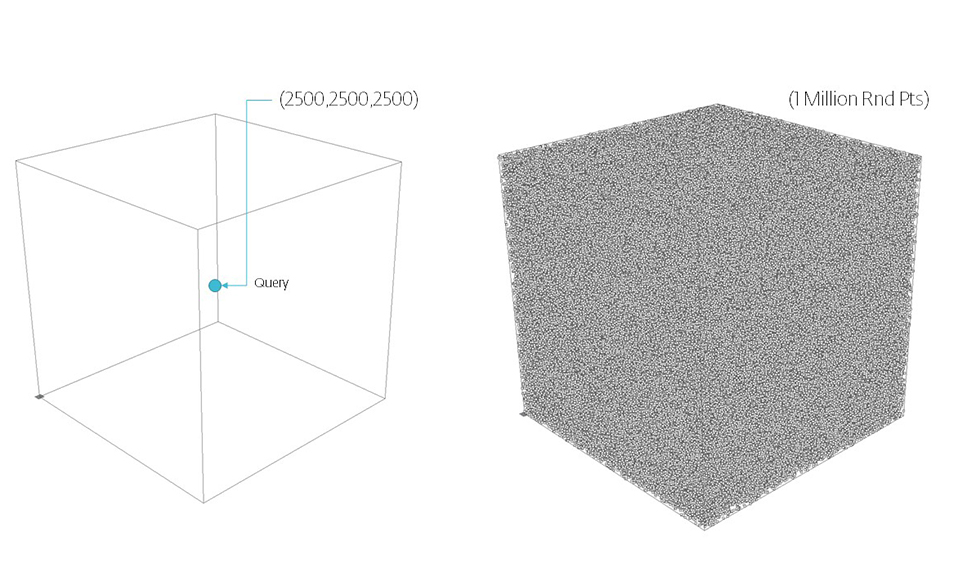
Calculation Time Comparison Between Code Versions in Seconds. Search Space Sampling 1 Million Points from 1 Point to find X nearest in a 500 unit radius then closest within that range. Searches 1 Million Points in a (5000,5000,5000) Unit Cube
RTREE Rhinocommon
- Tree Item Count = 1,000,000
- Found closest n point in 9 tests
- CALCULATION TIME TAKEN : 0.002 sec
- Search sphere size of 500
Rhinocommon Python
- Point Count = 1,000,000
- ClosestPoint = [2092.39 , 2955.144 , 2235.82]
- Number of Points in Range = 4151
- CALCULATION TIME TAKEN : 0.512 sec
- Search sphere size of 500
Rhinoscript Python
- Point Count = 1,000,000
- ClosestPoint = [2192.45 , 2958.38 , 2230.98]
- Number of Points in Range = 4236
- CALCULATION TIME TAKEN : 3.95 sec
RTREE Rhinocommon
- Tree Item Count = 1,000,000
- Number of Points in Range = 1
- CALCULATION TIME TAKEN : 0.00099 sec
Rhinocommon Python
- Point Count = 1,000,000
- Number of Points in Range = 1
- CALCULATION TIME TAKEN : 0.015 sec
Rhinoscript Python
- Point Count = 1,000,000
- Number of Points in Range = 1
- CALCULATION TIME TAKEN : 2.72 sec
RTREE Rhinocommon
- Mesh Vertex Count = 393,216
- Number of Agents = 50
- Iteration Steps = 200
- CALCULATION TIME TAKEN : 9.7 sec
- Search Radius = 4
Rhinocommon Python
- Mesh Vertex Count = 393,216
- Number of Agents = 50
- Iteration Steps = 200
- CALCULATION TIME TAKEN : 1390 sec
- Search Radius = 4
Rhinoscript Python
- Mesh Vertex Count = 393,216
- Number of Agents = 50
- Iteration Steps = 200
- CALCULATION TIME TAKEN : N/A Either Crashes or gave up because time was insanely long
- Search Radius = 4
Why the drastic difference in performance?
import Rhino
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
import scriptcontext
from System.Drawing import Color
import random as rnd
import time
"""--------------------------------------------------------
PERFORMANCE TEST - RTREE CLASS RHINOCOMMON
Repeated Search To Find Closest Neighbor
Search Sample = 1 Million Points
Search Radius = 500 Units
Search Space = Cube (5000,5000,5000)
--------------------------------------------------------"""
class SearchData:
def __init__(self, pts, point):
#Search Data class set up for instancing repeaded searching and tracking
self.HitCount = 0 #amount of times we searched starts with 0
self.arrPts = pts
self.Point = point
self.Index = -1 #insuring that we reduce the search radius after the first pass, see the conditional in searchcallback
self.Distance = 0
self.count = 0
def SearchCallback(sender, e):
data = e.Tag
data.HitCount += 1 #incrementing the hitcount
vertex = data.arrPts[e.Id] #the current closest neighbor
distance = data.Point.DistanceTo(vertex) #distance to the current closest neighbor from the query loc to define new search radius
if data.Index == -1 or data.Distance > distance: #condition to resize the search sphere to optimize the searching
e.SearchSphere = Rhino.Geometry.Sphere(data.Point, distance) #resize the search sphere
data.Index = e.Id #update the data.index to current point ID
data.Distance = distance #update the data.distance to the current distance
def RunSearch():
pttimeStart = time.time() #Start Timer
point = Rhino.Geometry.Point3d(5000/2,5000/2,5000/2)
intNumPts = 1000000 #specify the number of sample points to search
pts = []
tree = Rhino.Geometry.RTree() #create a new instance of the rtree class
for x in range(0,intNumPts):
randomPt = Rhino.Geometry.Point3d(rnd.random()*50000,rnd.random()*50000,rnd.random()*50000) #randomly place each point inside the 5k x 5k x 5k cube
pts.append(randomPt) #add the current point to the end of the pts list
tree.Insert(randomPt,x) #insert the current random point in the RTree at the specified index (x)
pttimeEnd = time.time() #end the timer
print "time taken to create pts: {}".format(pttimeEnd - pttimeStart) #print amount of time it took for calculations
print "TreeCount = {}".format(tree.Count) #count of the amount of items in the tree
timeStart = time.time() #Start Timer
data = SearchData(pts, point) #Create an instance of the Search Data Class passing sample list, query loc
sphere = Rhino.Geometry.Sphere(point, 500) #specify the inital search sphere size
if tree.Search(sphere, SearchCallback, data): #call the search method from the Rtree Class
print "Found point in {0} tests".format(data.HitCount) #print the amount of search iterations we did
print "ClosestPt = {}".format(data.arrPts[data.Index]) #print the closest neighbor
timeEnd = time.time() #end the timer
print "time taken: {}".format(timeEnd - timeStart) #print amount of time it took for calculations
if __name__=="__main__":
RunSearch()
Update
import Rhino
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
import scriptcontext
from System.Drawing import Color
import random as rnd
import time
"""--------------------------------------------------------
RHINOCOMMON METHODS
One Time Search to find all points within specified radius
The points found inside the specified radius get sampled for closest neighbor
No Repeat Search
Search Sample = 1 Million Points
Search Radius = 500 Units
Search Space = Cube (5000,5000,5000)
--------------------------------------------------------"""
def closestSearch(pts, point):
#function to sample point based on a search radius first then search for the closest inside that list mimic the rtree pass basically but with brute force
ptsinRange = [] #dynamic list to store points found inside initial search
for i, pt in enumerate(pts):
dist = point.DistanceTo(pt) #find the distance from each point to the query point
if dist < 500:
ptsinRange.append(pt) #if the distance is less than 500 append that point to the ptsinRange List
cPoint = Rhino.Collections.Point3dList.ClosestPointInList(ptsinRange,point) #search for the closest point from that list of points in range
if cPoint[0] == point[0] and cPoint[1] == point[1] and cPoint[2] == point[1]: #test against the closest neighbor being you
print "IS THE SAME"
return cPoint,ptsinRange #return the closest neighbor and the list of points in range
def RunSearch():
point = Rhino.Geometry.Point3d(5000/2,5000/2,5000/2)
intNumPts = 1000000 #specify number of sample points
pts = [] #store the random points in an empty list
for x in range(0,intNumPts):
randomPt = Rhino.Geometry.Point3d(rnd.random()*5000,rnd.random()*5000,rnd.random()*5000) #randomly place each point inside the 5k x 5k x 5k cube
pts.append(randomPt) #append each random point to the pts list
timeStart = time.time() #Start timer
data = closestSearch(pts, point) #call closestsearch function Pass query pt and list of points to search
print "ClosestPoint = {}".format(data[0]) #print the closest neighbor
print "Number of Pts in Range = {}".format(len(data[1])) #print how many points were captures inside the search radius
timeEnd = time.time() #stop the timer
print "time taken: {}".format(timeEnd - timeStart) #print the amount of time the calculations took
if __name__=="__main__":
RunSearch()
Update
import Rhino
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
import scriptcontext
from System.Drawing import Color
import random as rnd
import time
"""--------------------------------------------------------
RHINOSCRIPT METHODS USING PYTHON
One Time Search to find all points within specified radius
The points found inside the specified radius get sampled for closest neighbor
No Repeat Search
Search Sample = 1 Million Points
Search Radius = 500 Units
Search Space = Cube (5000,5000,5000)
--------------------------------------------------------"""
def closestSearch(pts, point):
#function to sample point based on a search radius first then search for the closest inside that list mimic the rtree pass basically but with brute force
ptsinRange = []#dynamic list to store points found inside initial search
for i in range(len(pts)):
dist = rs.Distance(pts[i],point)#find the distance from each point to the query point
if dist < 500:
ptsinRange.append(pts[i])#if the distance is less than 500 append that point to the ptsinRange List
cPointIndex = rs.PointArrayClosestPoint(ptsinRange,point)#search for the closest index from that list of points in range
cPoint = ptsinRange[cPointIndex] #find the closest point in the in range list from the index found above
if cPoint[0] == point[0] and cPoint[1] == point[1] and cPoint[2] == point[1]:#test against the closest neighbor being you
print "IS THE SAME"
return cPoint,ptsinRange #return the closest neighbor and the list of points in range
def main():
point = [5000/2,5000/2,5000/2]
intNumPts = 1000000#specify number of sample points
pts = []#store the random points in an empty list
for x in range(0,intNumPts):
randomPt = [rnd.random()*5000,rnd.random()*5000,rnd.random()*5000] #randomly place each point inside the 5k x 5k x 5k cube
pts.append(randomPt)#append each random point to the pts list
timeStart = time.time()#Start timer
data = closestSearch(pts, point)#call closestsearch function Pass query pt and list of points to search
print "ClosestPoint = {}".format(data[0])#print the closest neighbor
print "Number of Pts in Range = {}".format(len(data[1]))#print how many points were captures inside the search radius
timeEnd = time.time()#stop the timer
print "time taken: {}".format(timeEnd - timeStart)#print the amount of time the calculations took
main()
Update
Recently in Portfolio
- [K]ernels

- Nike A.I.R Prototypes

- [A]nisochromatic Meshing

- Nike After Dark Tour

- PARAPRAXIS
- [001.HRR] CONCEPT BIKE

- 2040:LUNAR.OUTPOST[a]
- HE.6 2020 Prototype

- CULEBRA.NET

- PYTORCH-CLASSIFIER
- Nike Zoom Superfly Elite

- BENGBU CITY OPERA

- Nike Footscape Flyknit DM

- Jordan Hyperdunk React

- KA-HELMET

- [C]ucarachas

- [S]eeker
- [O]h Baby
- [E]l Papa

- [S]hatter.Brain

- [S]tigmergy
- [F]orces
- CULEBRA.JAVA

- [C]ulebra.MultiBehaviors

- [S]ticky Stuff
- [S]entinels
- [G]allopingTopiary
- RELUXOED

- [SRC] . Semi Rigid Car

- [P]erlin

- [E]ternal Wanderers
- [W]heelie

- [S]labacube

- [M]esh Crawlers

- [L]a Silla
- [3]D BabyMaking Trackstars
- [3]D Trackers
- [2]D BabyMaking Trackers
- [T]rackers
- CULEBRA GRASSHOPPER

- culebra.[M]eshCrawlers.3D

- culebra.[H]ybrid.3D

- culebra.[F]lorgy

- culebra.[F]ockers.3D
- culebra.[F]ockers.2D

- culebra.[N]oisey.3D

- [E]l Nino

- culebra.[S]elfOrg

- [D]rippin

- culebra.[N]oisey.2D

- [C]reepyCrawlers

- [J]eepresesCreepers

- [T]2000

- PUFFER PLEATNESS

- EMERGEN[CY]

- [L]iquified

- [S]uckedComp

- [X]plosion
- MR. EW

- [H]airGoo
- [B]alled
- [n]injaStars

- [b]loomer

- [t]rip city

- TAPE GUNNED
- [B]oom

- [M]iller Time
- [D]elamjam

- [B]rain Zapper
- [B]ig Bird
- [E]gg Tube Pavillion
- [A]llice’s Easter Tree
- [S]weet Honey
- [U]M.Urgent

- [t]oo.urgent

- [B]onnie..+..Clyde
- [B]io Mess
- [EL]Mojado.Virus
- [W]HAT the …!
- [H]ot Lava
- [P]leat Diddy
- [t]erminator easter egg
- Mr. BB
- [B]less You

- [F]antastic + Interactive
- [S]oo_Minimally_Pathed
- [P]uffer Fish.Fab
- [M]an Eater

- [AHH] Alien House Hunters

- [W]eave Machine
- Sportbike Racing

- Grappling

- Kart Racing




Leave a reply